iframe refused to connect
Introduction
Localhost refused to connect is a common error that may occur when working on a local automobile. In this commodity, you volition learn the almost mutual causes of the localhost refused to connect fault and how to resolve information technology.

What is the Localhost Refused to Connect Error?
Localhost is a loopback address used for testing and developing on a local machine. When a user pings localhost, the request remains on the local network and connects to the machine in apply. If such a connexion is not possible, the browser displays an error bulletin:
localhost refused to connect.
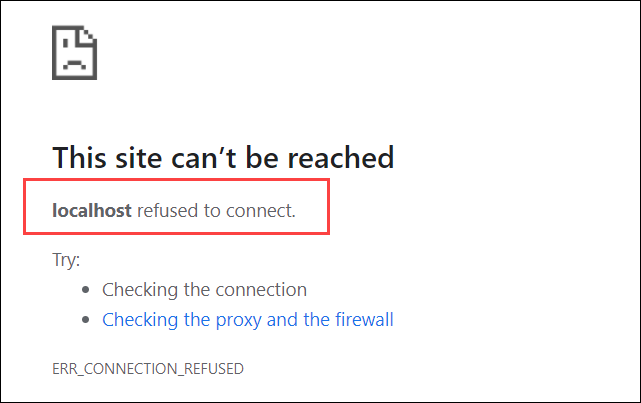
The localhost refused to connect message displays i of two possible errors:
- ERR_CONNECTION_REFUSED (the server rejected the request for connection)
- ERR_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT (the server has not responded to the request and the customer is still waiting for a response)
What Causes the Localhost Refused to Connect Error
Common causes that effect in localhost refusing to connect:
- The server being blocked by the firewall.
- Localhost doesn't resolve to 127.0.0.one.
- Apache declining to run properly.
- DNS failing to function.
- The server beingness accessed from the wrong port.
- The browser settings blocking the connection.
To solve the event, place the source of the fault. The best way to do then information technology to exam out each probable cause, starting from the most frequent ones.
How to Solve the Localhost Refused to Connect Error?
The sections below provide methods to resolve the localhost refused to connect error.
Temporary Disable the Firewall
Check whether the firewall settings are blocking the localhost connection past disabling the firewall temporarily. (For Bone-specific instructions, see sections below.)
Once y'all disable the firewall, navigate to localhost in a browser to check whether it connects. If localhost still refuses to connect, move on to other potential causes. Also, make sure to plow on the firewall once you lot take finished working with localhost.
Disable Firewall on Linux
The firewall configuration tool on Linux systems varies depending on the distro. While Ubuntu and Debian distributions utilise UFW, CentOS and RHEL systems use firewalld by default.
To disable the UFW firewall on Ubuntu/Debian, open up the concluding window and run:
sudo ufw disable Check the status by running:
sudo ufw condition 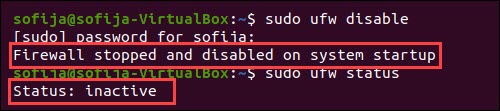
To disable firewalld on CentOS/RHEL, use the control:
sudo systemctl stop firewalld Verify the status is inactive by running:
sudo systemctl status firewalld 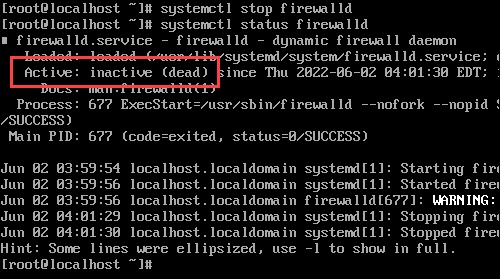
Disable the Firewall on Mac OS
1. Click the Apple tree icon in the upper-left corner to open the menu and select System Preferences.
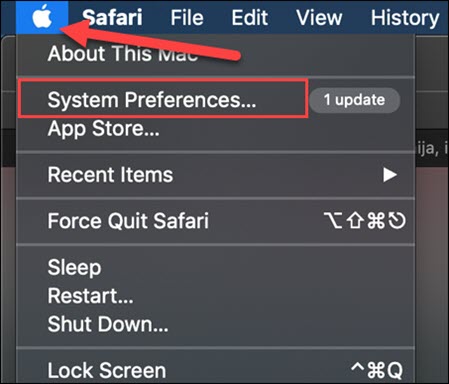
2. Navigate to Security and Privacy settings and movement to the Firewall tab.
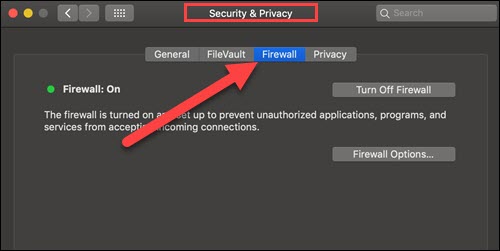
3. If the lock at the bottom left of the pane is locked, click the icon to unlock the preference pane. Type in your password to ostend.
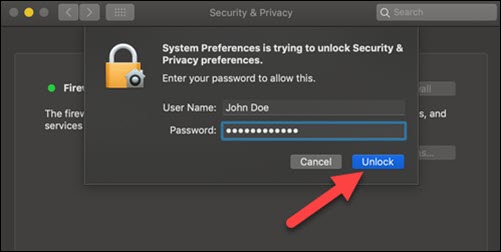
4. Click Turnoff Firewall to complete the process.
Disable the Firewall on Windows
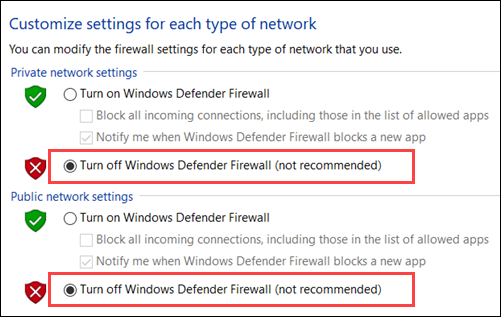
1. Open up the Windows Control Console and click the Windows Defender Firewall icon.
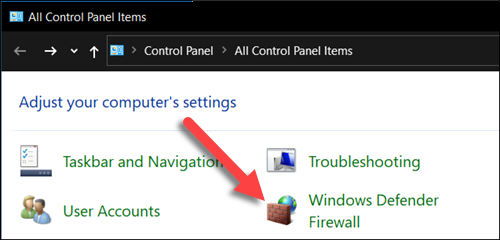
ii. Select Turn Windows Defender Firewall on or off from the menu on the left side of the window.
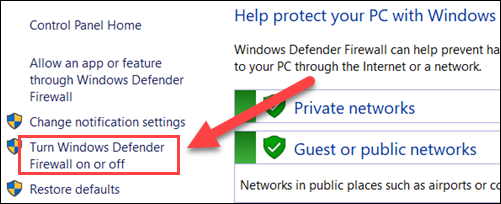
3. Finally, check the Turn off Windows Defender Firewall checkbox and click OK.
Check Localhost IP Address
Localhost and the IP address 127.0.0.1 are not completely synonymous. In most cases, 127.0.0.1 is used for loopback, all the same not exclusively. For case, IPv6 systems link the localhost to the address : :ane.
Additionally, if the host file has been modified, the localhost could link to a different IP accost.
Attempt typing both localhost and 127.0.0.ane in the browser search bar, in case of a connectedness error.
Check Apache Server Status
Another of import factor for accessing the localhost is that the Apache server is running properly. Therefore, if the arrangement rejects the connectedness, it is necessary to bank check Apache's condition.
The control for verifying whether Apache is running on a Linux OS depends on the distribution in employ. Follow the steps beneath and employ the advisable control.
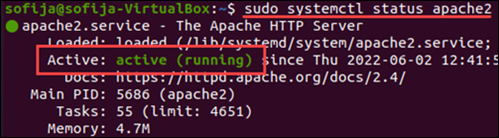
1. Verify Apache condition with the command:
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo systemctl status apache2 CentOS/RHEL:
sudo systemctl status httpd The output should display that Apache is agile (running), as in the image beneath. If that is the instance, the Apache server is working correctly and you can move to the next probably cause for error.
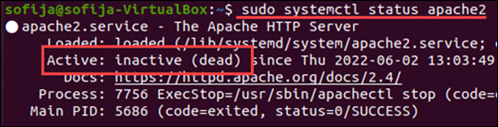
two. If Apache is not running properly, the output displays that its status is inactive (dead).
3. To fix the outcome, try restarting the Apache service using:
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo systemctl restart apache2 CentOS/RHEL:
sudo systemctl restart httpd four. Bank check the Apache status once again:
Ubuntu/Debian:
sudo systemctl status apache2 CentOS/RHEL:
sudo systemctl status httpd 5. If the condition remains inactive, move on to deleting and reinstalling Apache on the organization:
- Install Apache on Ubuntu
- Install Apache on CentOS
Flush the DNS
DNS cache is stored to speed upwards loading of previously visited websites. If DNS collects likewise many records or some of the records get corrupt, it may neglect to function. Such an issue can result in localhost refusing to connect.
The best way to ensure DNS is not preventing the localhost connexion is to clear the DNS cache and delete all saved DNS lookup data.
The steps for flushing the DNS vary depending on the Bone in use. For detailed instructions, refer to How to Flush DNS Cache in macOS, Windows, & Linux.
Linux:
sudo /etc/init.d/nscd restart MacOS:
sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder Windows:
ipconfig /flushdns Modify Port Settings
By default, localhost uses port number 80. If another application is using the aforementioned port, it can create a conflict resulting in localhost refusing to connect.
Change Port Number on XAMPP
If you are using the XAMPP stack, follow the steps beneath:
1. Open the XAMPP command console and click on the Netstat push button.
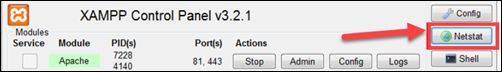
2. Netstat opens a listing of all TCP listening sockets. If port fourscore is already in use by some other application, move on to choosing a gratis port for Apache.
3. Before proceeding to the next step, make sure to stop the Apache service.
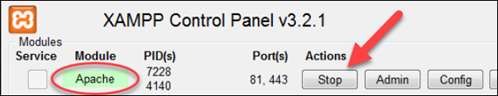
4. Locate and open up the httpd.conf file. The location of the file varies depending on the OS:
- Linux users will find it in bin/apache.
- Windows stores the file in C:\xampp\apache\conf.
- The path to the file on Mac OS is Applications/XAMPP/xamppfiles/etc/httpd.conf.
v. Find the following lines in the file:
Listen 80 ServerName localhost:80 6. Modify the port number to any other gratis port. In this instance, we alter it to 8080.
Listen 8080 ServerName localhost:8080 vii. Salvage and exit the file. Restart the Apache spider web server in the XAMPP control console and effort connecting to localhost again.
Change Port Number on WAMPP
If you are using the WAMP software stack and want to change the Apache port:
i. First, stop all instances running in WAMP with the End Task button.
ii. And then, open the httpd.conf file located in C:\wamp\apache2\conf.
iii. Locate the following lines in the file:
Heed 80 ServerName localhost:fourscore 4. Alter the port number to a complimentary port (8080 for example).
Listen 8080 ServerName localhost:8080 5. Relieve the changes and exit the file.
Check Browser Settings
Make sure the browser is not responsible for causing the localhost mistake.
Commencement by navigating to localhost in a different browser. If the connexion establishes, then the settings in the initial browser are the issue.
Frequently, browsers automatically redirect HTTP addresses to HTTPS causing the localhost refused to connect mistake.
Modify DNS Settings in Chrome
1. To modify the default setting on Chrome, paste the following URL in the address bar: chrome://net-internals/#hsts
two. Then, open up the Domain Security Policy tab and scroll downwardly to the Delete domain security policies section.
3. Add localhost as the domain name and click Delete.
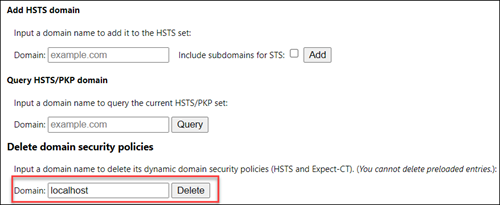
4. Restart the browser to apply the changes.
Alter DNS Settings in Firefox
1. Open the Application Menu in the pinnacle right corner of the browser window and select Settings.
ii. Navigate to Privacy & Security and scroll down to the HTTPS-Just Mode section.

3. To apply the changes, reopen the browser.
Determination
Afterwards reading this article, yous should know the steps to locate the cause and set the localhost refused to connect mistake.
Another mutual issue that occurs when working locally on software stacks such as LAMP, WAMP, and others is the Admission denied for user root@localhost error. Follow the link to troubleshoot Access denied for user root@localhost error in a few simple steps.
Was this commodity helpful?
Yes No
Source: https://phoenixnap.com/kb/localhost-refused-to-connect

0 Response to "iframe refused to connect"
Post a Comment